Zone List
To create or modify a zone, go to
Ribbon: Zone List
Pulldown Menu:
Zones Dialog Box
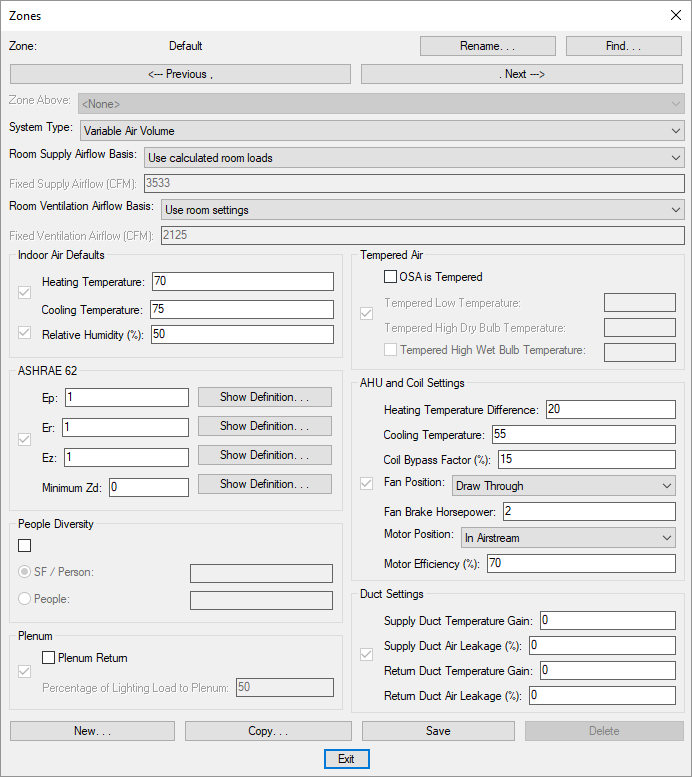
See the Common Schedule Dialog Box Features section for more information about how this dialog box works. This section describes the , , , , , , , and buttons.
-
Zone Above: ▾ The zone that is above this zone in the zone hierarchy.
- <None> No zone is above this zone. All of the other sections in this dialog box will be available to be set.
- Other Zone There is a zone above this zone. By default, most of the settings for the current zone are based upon the selected Zone Above.
-
System Type: ▾ The type of system that is modeled by the zone.
- Variable Air Volume The system is a variable air volume system. The peak zone values will be coincident peaks, sometimes referred to as the block load.
- Constant Volume The system is a constant volume system. The peak zone values will be a sum of the room peak values.
-
Room Supply Airflow Basis ▾ How the room supply airflow is calculated.
- Use calculated room loads The room supply airflow is based upon the calculated room load.
- Prorate using fixed supply airflow The room supply airflow is prorated based upon the Fixed Supply Airflow. The supply airflow based upon the calculated room load is compared with the fixed supply airflow. Each room is then adjusted up or down based upon this ratio. The total supply air for all of the rooms will equal the Fixed Supply Airflow.
-
Fixed Supply Airflow: The total airflow to be supplied to the zone when Room Supply Airflow Basis ▾ is set to Prorate using fixed supply airflow. This field is disabled if Room Supply Airflow Basis ▾ is set to Use calculated room loads.
-
Room Ventilation Airflow Basis: ▾ How the room ventilation airflow is calculated.
- Use room settings The room ventilation airflow is based upon the room settings.
- Use fixed ventilation airflow The room ventilation airflow is based upon the Fixed Ventilation Airflow. The total ventilation for all of the rooms will equal the Fixed Ventilation Airflow.
-
Fixed Ventilation Airflow: The total ventilation for the zone when Room Ventilation Airflow Basis ▾ is set to Use fixed ventilation airflow. This field is disabled if Room Ventilation Airflow Basis ▾ is set to Use room settings.
Indoor Air Defaults
The Indoor Air Defaults section sets the default temperature and humidity values for rooms in the zone. These values can be overridden for specific room types or individual rooms.
If Zone Above ▾ is set to <None>, these values must be entered manually.
If Zone Above ▾ has a zone selected, these values are set based upon the above zone. Check the first box beside this section to specify a different Heating Temperature and/or Cooling Temperature for this zone. Check the second box beside this section to specify a different Relative Humidity for this zone.
-
Heating Temperature: The goal temperature when heating rooms in the zone.
-
Cooling Temperature: The goal temperature when cooling rooms in the zone.
-
Relative Humidity: The goal relative humidity when cooling rooms in the zone.
ASHRAE 62
The ASHRAE 62 section sets values that are used when performing the ASHRAE 62.1 zone ventilation calculation.
If Zone Above ▾ is set to <None>, these values must be entered manually.
If Zone Above ▾ has a zone selected, these values are set based upon the above zone. Check the box beside this section to specify different values for this zone.
The descriptions for these values are based upon ASHRAE 62.1-2004, Appendix A: Definitions.
-
Press this button next to each value to display the ASHRAE 62.1 definition for the value.
-
Ep: Primary air fraction to the zone.
For single-duct and single-zone systems, set Ep to 1.
-
Er: In systems with secondary recirculation of return air, fraction of secondary recirculated air to the zone that is representative of average system return air rather than air directly recirculated from the zone.
For plenum return systems with local secondary recirculation (e.g., fan-powered VAV with plenum return), set Er less than or equal to 1.
For ducted return systems with local secondary recirculation (e.g., fan-powered VAV with ducted return), Er is typically set to 0.
-
Ez: A measure of how effectively the zone air distribution uses its supply air to maintain acceptable air quality in the breathing zone. Depending upon your system, set Ez to the recommended value:
- Ceiling supply of cool air: 1
- Ceiling supply of warm air and floor return: 1
- Ceiling supply of warm air 15°F or more above space temperature and ceiling return: 0.8
- Ceiling supply of warm air less than 15°F above space temperature and ceiling return, provided that the 150 fpm supply air jet reaches to within 4.5 ft of floor level: 1
- For lower velocity supply air: 0.8
- Floor supply of cool air and ceiling return, provided that the 150 fpm supply jet reaches 4.5 ft or more above the floor (Note: most underfloor air distribution systems comply with this provision): 1
- Floor supply of cool air and ceiling return, provided low-velocity displacement ventilation achieves unidirectional flow and thermal stratification: 1.2
- Floor supply of warm air and floor return: 1
- Floor supply of warm air and ceiling return: 0.7
- Makeup supply drawn in on the opposite side of the room from the exhaust and return: 0.8
- Makeup supply drawn in near to the exhaust and return location: 0.5
-
Minimum Zd: The minimum discharge outdoor air fraction for the zone.
The formal definition is . is the zone outdoor airflow. is the zone discharge airflow.
For non-VAV systems, set this value to 0.
For VAV systems, is the minimum expected discharge airflow for design purposes. You must determine what the minimum discharge outdoor air fraction for the system will be. The Minimum Zd you specify implicitly defines the minimum for the zone.
People Diversity
The People Diversity section sets whether the number of people in the zone is diversified compared to the number of people in the rooms in the zone.
If the checkbox is unchecked, the number of people in the zone is the sum of the number of people in the rooms in the zone.
If the checkbox is checked, the number of people in the zone is based upon the 🔘 SF / Person or 🔘 People setting. The people load in the zone will be adjusted accordingly.
-
🔘 SF / Person: Select this option to set the number of people in the zone based upon the zone area.
-
🔘 People: Select this option to set the total number of people in the zone.
Plenum
The Plenum section controls whether the zone has a plenum return. When a zone has a plenum return, some of the room loads are moved to the system load instead. These include the roof load, the portion of the wall load that is above the plenum, and a percentage of the lighting load.
If Zone Above ▾ is set to <None>, these values can be entered manually.
If Zone Above ▾ has a zone selected, these values are set based upon the above zone. Check the box beside this section to specify different values for this zone.
-
☐ Plenum Return Whether the zone has a plenum return.
-
Percentage of Lighting Load to Plenum: For zones with a plenum return, the percentage of the lighting load that is transferred to the plenum. The lighting load in the plenum is included in the system load but not the room load.
Tempered Air
The Tempered Air section controls whether the zone has tempered air and the settings of the tempered air if it does.
If Zone Above ▾ is set to <None> these values can be entered manually.
If Zone Above ▾ has a zone selected, these values are set based upon the above zone. Check the box beside this section to specify different values for this zone.
-
☐ OSA is Tempered Whether the outside air is tempered before it reaches the air handler.
-
Tempered Low Temperature: If ☐ OSA is Tempered is checked, this temperature is used instead of the OSA Low Temperature Dry Bulb temperature in the Project Info command when calculating heating loads.
-
Tempered High Dry Bulb Temperature: If ☐ OSA is Tempered is checked, this temperature is used instead of the OSA High Dry temperature in the Project Info command when calculating cooling loads.
-
☐ Tempered High Wet Bulb Temperature: Whether the web bulb temperature is tempered in addition to the dry bulb temperature. If this is checked, this temperature is used instead of the OSA High Wet temperature in the Project Info command when calculating cooling loads.
AHU and Coil Settings
The AHU and Coil Settings section controls values that are used in the supply air requirements calculations and the psychrometric calculations.
If Zone Above ▾ is set to <None> these values must be entered manually.
If Zone Above ▾ has a zone selected, these values are set based upon the above zone. Check the box beside this section to specify different values for this zone.
-
Heating Temperature Difference: The difference between the heating temperature in the room or zone and the temperature of the air at the supply diffusers. This temperature difference is used as an input in the heating supply air requirement calculations.
-
Cooling Temperature: The temperature of the air at the supply diffusers. This temperature is used as the desired end condition for the psychrometric calculations and as an input in the cooling supply air requirements calculations.
-
Coil Bypass Factor: The percentage of air that is not conditioned by the coil.
-
Fan Position: ▾ Where the fan is positioned relative to the coil.
- Blow Through The fan is positioned before the coil. This location requires a higher coil dew point temperature.
- Draw Through The fan is positioned after the coil. This location requires a lower coil dew point temperature.
-
Fan Brake Horsepower: The horsepower of the fan brake.
-
Motor Position: ▾ Where the motor is positioned relative to the ductwork.
- In Airstream The motor is positioned in the ductwork. The temperature gain from the motor is included in the psychrometric calculations.
- Out of Airstream The motor is positioned outside the ductwork. The temperature gain from the motor is not included in the psychrometric calculations.
-
Motor Efficiency: The efficiency of the motor. Higher values result in lower temperature gains from the motor.
Duct Settings
The Duct Settings section controls values in the ductwork that are used in the psychrometric calculations.
If Zone Above ▾ is set to <None> these values must be entered manually.
If Zone Above ▾ has a zone selected, these values are set based upon the above zone. Check the box beside this section to specify different values for this zone.
-
Supply Duct Temperature Gain: The change in temperature of the air traveling through the supply ductwork. This temperature gain is often caused by ductwork in unconditioned spaces, typically outside.
An increase in this value results in a lower coil dew point temperature.
-
Supply Duct Air Leakage: The percentage of supply air that is leaked out of the ductwork. This air is leaked outside the building. Do not include air that is leaked out of the ductwork but remains inside the building.
An increase in this value results in an increase in the mixed air volume. If the amount of air leaked exceeds the outside air volume, it will increase the volume of outside air required.
-
Return Duct Temperature Gain: The change in temperature of the air traveling through the return ductwork. The temperature gain is often caused by ductwork in unconditioned spaces, typically outside.
An increase in this value results in a higher mixed air temperature and a higher coil dew point temperature.
-
Return Duct Air Leakage: The percentage of return air that is leaked out of the ductwork. This air is leaked outside the building. Do not include air that is leaked out of the ductwork but remains inside the building.
An increase in this value results in an increase in the outside air volume.