How Building Angle Affects Calculations
When I have my feeder length measurement or branch circuit length measurement set to Right Angles, I have the option to set a Building Angle as well. How is this value used, and how does it affect wire length and other calculations?
The Right Angles wire length measurement is used to simulate running the wire through the walls of the building, rather than in a straight line.
To get accurate calculations, you need to tell the software how the walls are oriented. Setting the Building Angle does this by offsetting the orientation of walls relative to the Design Master Electrical alignment point.
When the Building Angle is set to 0, the walls are assumed to be parallel and perpendicular to the alignment point—in other words, running north-south and east-west. The wire lengths are calculated accordingly, as shown below.
Increasing the Building Angle value will offset the walls in a counterclockwise direction. Setting it to 45 will result in wires that run southwest-northeast and northwest-southeast, as shown below.
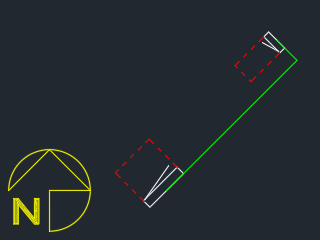
Having an incorrect Building Angle can significantly impact wire length calculations, which will affect fault and voltage drop calculations in turn. The examples above use the same start and end points, but return 31' for the first calculation and 26' for the second—a 17.5% difference.